NABARD Grade A Notification 2023
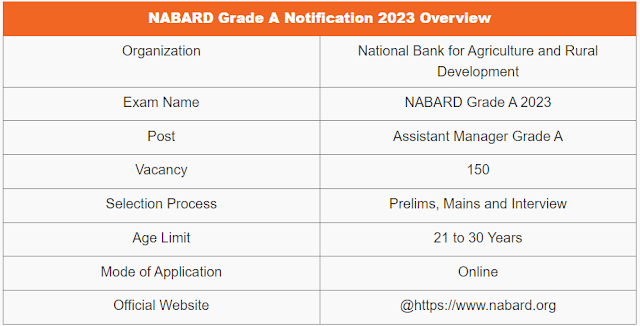
NABARD Grade A Notification 2023 has been released on 02nd September 2023 for 150 Assistant Manager "Grade A" vacancies. Applications are invited from Indian citizens for the post of Assistant Manager in Grade ‘A’ in the Rural Development Banking Service (RDBS) in National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD). Candidates can apply only ON-LINE on NABARD website www.nabard.org between 02 September 2023 and 23 September 2023. NABARD is an all India Apex Organization, wholly owned by Government of India and is an equal opportunity employer.
NABARD Grade A Recruitment : Different Posts/Discipline
Recruitment to the post of Assistant Manager in Grade ‘A’ (RDBS) - There are are total Elevan Different Posts under Assistant Manager (RDBS).
NABARD Grade A 2023 Notification Explained
NABARD Grade A 2023 Syllabus and Study Plan Explained
NABARD Grade A Recruitment : Eligibility Criteria
Educational Qualification (Cut off Date will be Announced in Official Notification)
a) A candidate can apply for Assistant Manager (RDBS/Rajbhasha) under only one option from among the options given in Table. It is clarified that candidate applying for Asst. Manager (RDBS) - General cannot apply for another discipline and vice versa.
b) The candidate can apply only for ONE Post/Discipline of his / her choice. In case of multiple applications across or within disciplines for Grade A (RDBS), only the last application submitted will be considered valid and fee against all other applications will be forfeited.
c) PWBD candidates applying against Unreserved (UR) posts will not be eligible for relaxation in percentage in Educational Qualification. They may, however, be eligible for relaxation in Age and Fee.
d) The candidate must possess the required educational qualification as on 01-09-2023. The result of final term / semester/ year examination of the required educational qualification must have been declared on or before 01-09-2023 In other words, candidates whose final year/semester results have been declared on or after 02-09-2023 are not eligible to apply. (This is the cut off Date of Last Year, for this year wait for official Notification)
Bachelor’s Degree in a particular discipline means that the candidate must have studied that discipline as main subject in respective degree course and it must be mentioned in the Degree Certificate issued by the University/Institute.Assistant Manager in Grade ‘A’ (RDBS) : Post Wise Qualification
I. General : Bachelor’s Degree in any subject from a recognized University with a minimum of 60% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants - 55%) in aggregate OR Post Graduate degree, MBA/PGDM with a minimum of 55% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants - 50%) in aggregate OR CA/ CS/ICWA OR Ph.D from Institutions recognized by GOI/UGC .
II. Fisheries : Bachelor’s degree in Fisheries Science from a recognized University/Institution with 60% marks (SC/PWBD applicants 55%) in aggregate OR Post graduate degree in Fisheries Science with 55% marks (SC/PWBD applicants 50%) in aggregate.
III. Forestry : Bachelor’s degree in Forestry from a recognized University/Institution with 60% marks (SC/PWBD applicants - 55%) in aggregate OR Post graduate degree in Forestry with 55% marks (SC/PWBD applicants - 50%) in aggregate.
IV. Finance : BBA (Finance/Banking) / BMS (Finance/Banking) with 60% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants - 55%) OR Two years full time P.G. Diploma in Management (Finance) / Fulltime MBA (Finance) degree with 55% (SC/ST/PWBD applicants - 50%) from Institutions / Universities recognized by GoI /UGC with Bachelor's Degree in any discipline.
Candidates will be required to submit a certificate from Institution/University regarding specialization in finance OR Bachelor of Financial and Investment Analysis with 60% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants - 55%) OR Bachelor’s degree in any discipline from a recognized University/Institution with Membership of Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI). The Membership of ICAI must have been obtained on or before 01-07-2021 OR CFA.
V. Computer and Information Technology: Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science/ Computer Technology/ Computer Applications/Information Technology with 60% marks (SC/PWBD applicants 55%) in aggregate OR a post graduate degree in Computer Science/ Computer Technology/ Computer Applications/Information Technology with 55% marks (SC/PWBD applicants 50%) in aggregate from a recognized university.
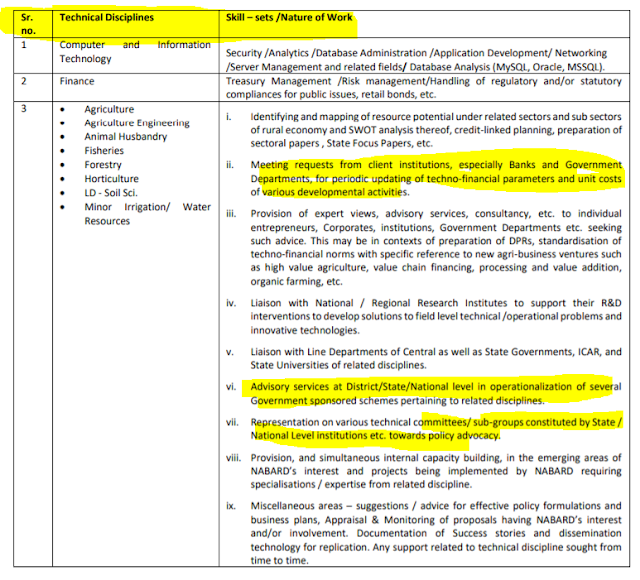
NABARD Grade A : Roles and Responsibilities
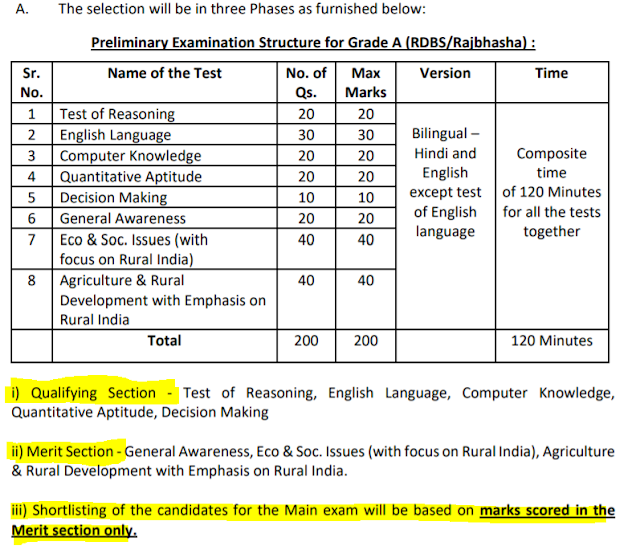
NABARD Grade A : Selection Ratio
The calling Ratio to qualify for the main examination and interview would be a maximum of 1:25 and 1:3, respectively. The ratio may be suitably reduced at the discretion of the bank. Candidates who qualify and rank sufficiently high as decided by NABARD, shall be called for appearing at the Main Examination and Interview
NABARD Grade A Exam : New Syllabus for ESI & ARD
NABARD Grade A Syllabus: Economic & Social Issues
Nature of Indian Economy - Structural and Institutional features - Economic underdevelopment - Opening up the Indian Economy - Globalization - Economic Reforms in India - Privatization.
Inflation - Trends in Inflation & their Impact on National Economy and Individual Income.
Poverty Alleviation and Employment Generation in India - Rural and Urban - Measurement of Poverty - Poverty Alleviation Programmes of the Government.
Population Trends - Population Growth and Economic Development - Population Policy in India.
Agriculture - Characteristics / Status - Technical and Institutional changes in Indian Agriculture - Agricultural performance - Issues in Food Security in India - Non Institutional and Institutional Agencies in rural credit.
Industry - Industrial and Labour Policy - Industrial performance - Regional Imbalance in India's Industrial Development - Public Sector Enterprises.
Rural banking and financial institutions in India - Reforms in Banking/ Financial sector.
Globalization of Economy - Role of International Funding Institutions - IMF & World Bank - WTO - Regional Economic Co-operation.
Social Structure in India - Multiculturalism - Demographic trends - Urbanization and Migration - Gender Issues Joint family system - Social Infrastructure - Education - Health and Environment.
Education - Status & System of Education - Socio -Economic Problems associated with Illiteracy - Educational relevance and educational wastage - Educational Policy for India.
Social Justice - Problems of scheduled castes and scheduled tribes - socio-economic programmes for scheduled castes and scheduled tribes and other backward classes. Positive Discrimination in favour of the under privileged - Social Movements - Indian Political Systems - Human Development.
NABARD Grade A Exam : Agriculture and Rural Development
Agriculture : Definition, meaning and its branches, Agronomy: definition, meaning and scope of agronomy. Classification of field crops. Factors affecting on crop production, Agro Climatic Zones;
Cropping Systems : Definition and types of cropping systems. Problems of dry land agriculture; Seed production, seed processing, seed village;
Meteorology : weather parameters, crop-weather advisory; Precision Farming, System of Crop Intensification, organic farming;
Soil and Water Conservation : Major soil types, soil fertility, fertilizers, soil erosion, soil conservation, watershed management;
Water Resource : Irrigation Management: types of irrigation, sources of irrigation, crop-water requirement, command area development, water conservation techniques, micro-irrigation, irrigation pumps, major, medium and minor irrigation.
Animal Husbandry : Farm animals and their role in Indian economy, Animal husbandry methods in India, common terms pertaining to different species of livestock, Utility classification of breeds of cattle.
Introduction to common feeds and fodders, their classification and utility. Introduction to poultry industry in India (past, present and future status), Common terms pertaining to poultry production and management. Concept of mixed farming and its relevance to socio-economic conditions of farmers in India.
Complementary and obligatory nature of livestock and poultry production with that of agricultural farming.
Fisheries: Fisheries resources, management and exploitation - freshwater, brackish water and marine; Aquaculture- Inland and marine; biotechnology; post-harvest technology. Importance of fisheries in India. Common terms pertaining to fish production.
Agriculture Extensions: Its importance and role, methods of evaluation of extension programmes, Role of Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) in dissemination of Agricultural technologies.
Plantation & Horticulture: Definition, meaning and its branches. Agronomic practices and production technology of various plantation and horticulture crops. Post-harvest management, value and supply chain management of Plantation and Horticulture crops.
Forestry: Basic concepts of Forest and Forestry. Principles of silviculture, forest mensuration, forest management and forest economics. Concepts of social forestry, agroforestry, joint forest management.
Forest policy and legislation in India, India State of Forest Report 2015. Recent developments under Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Farm and Agri Engineering : Farm Machinery and Power, Sources of power on the farm- human, animal, mechanical, electrical, wind, solar and biomass, bio fuels, water harvesting structures, farm ponds, watershed management, Agro Processing, Controlled and modified storage, perishable food storage, godowns, bins and grain silos.
Ecology and Climate Change: Ecology and its relevance to man, natural resources, their sustainable management and conservation. Causes of climate change, Greenhouse Gases (GHG), major GHG emitting countries, climate analysis, distinguish between adaptation and mitigation, climate change impact to agriculture and rural livelihood, carbon credit, IPCC, UNFCCC, CoP meetings, funding mechanisms for climate change projects, initiatives by Govt of India, NAPCC, SAPCC, INDC.
Present Scenario of Indian Agriculture and Allied activities : recent trends, major challenges in agriculture measures to enhance viability of agriculture. Factors of Production in agriculture; Agricultural Finance and Marketing; Impact of Globalization on Indian Agriculture and issues of Food Security; Concept and Types of Farm Management.
NABARD Grade A Exam : Rural Development Syllabus
Rural Development: Concept of Rural Area, Structure of the Indian Rural Economy Importance and role of the rural sector in India- Economic, Social and Demographic Characteristics of the Indian rural economy, causes of Rural Backwardness.
Rural population in India : Occupational structure, Farmers, Agricultural Laborers, Artisans, Handicrafts, Traders, Forest dwellers/tribes and others in rural India- Trends of change in rural population and rural work force; problems and conditions of rural labor; Issues and challenges in Hand looms
Panchayati Raj Institutions – Functions and Working. MGNREGA, NRLM – Aajeevika, Rural Drinking water Programmes, Swachh Bharat, Rural Housing, PURA and other rural development programmes.
Buy NABARD Grade A 2023 Guidance and Mentorship Program @1699 (3-in-1) - Buy Here
Or, Buy NABARD Grade A 2023: PIB + Descriptive Mock Test @Rs.1199/ (2-in-1) - Buy Here
Or, Buy NABARD Grade A 2023: PIB Summary & Analysis Subscription @Rs.599/- Buy Here
How to Join NABARD Grade A Telegram Channel for Updates and Study Materials
Step - 1. Download Telegram App From Play store.
Step - 2. Login with Your Mobile Number.
Step - 3. Search @agrilearn_nabard the Search Box to Join Group.
Step - 4. Click Here to Join